What is microcomputer? | PCB, Microprocessor, Software, Hardware,?
Main contents:
·
What is a microcomputer?
·
What is Printed Circuit Board PCB)
·
Structure of a computer
·
What are the main components of a computer?
·
Structure of a CPU
·
Schematic diagram of a mainboard
·
What is a microprocessor?
·
Impacts of the microprocessor
·
CPU vs. Microprocessor
·
What are the applications of microprocessors?
·
Main memory
·
Storage
·
What is hardware
·
What is software
·
What are the differences between hardware and software?
What is a Microcomputer?
A small, and a bit inexpensive computer with a microprocessor as its central processing unit (CPU). It includes a microprocessor, memory, and minimal input/output (I/O) designed through circuit connections on a single printed circuit board (PCB
What is PCB (Printed Circuit Board)?
A photo of one side of a motherboard PCB, which shows conductive traces and solder points for through-hole components on the opposite side is shown below;
·
1mm-25mm on a side
·
100-1000M transistors
·
25-250M “logic gates”
The structure of a computer;
|
Computer(communication
lines, Peripherals) |
Systems interconnection |
Central Processing Unit |
|
Main Memory |
||
|
Input/ Output |
What are the main features of a
computer?
Four main components
of computer structure:
Central Processing
Unit (CPU): controls computer performance and performs its data processing
functions; commonly referred to as a processor.
Greater memory:
saves data
Ø Input/output I /
O): transfers data between a computer and its external environment.
ERC System
Connectivity: The method of communication between CPU, memory, and Input / The output I / O).
What is the difference between Input
/ Output and Communication Lines?
When data is received from or transmitted by a device
directly connected to a computer, the process is called Input/Output (I / O).
When data is transmitted over long distances to or from a
remote device, the process is known as Data Communication.
· Mainboard: integrated circuits (ICs)
Ø CPU (Central Processing Unit)
Chip Partner chipset, e.g., GPU [card slot] (in the absence
of an integrated GPU)
Ø Memory, e.g., RAM
Chip Peripheral I / O chip (e.g., USB, IDE, IEEE11394).
 |
| Inside a PC. |
·
sto Storage Device (SSD, NVME SSD, HDD)
Hard disk, CD-RW DVD-RW, (floppy disk)
·
Chassis
Hold boards
Power supply unit
A physical interface for the user and other
systems.
·
Cooling
(CPU, Chassis)
Air-cooled, Liquid-cooled.
·
Display
device, Monitor
·
Input
devices, Mouse, Keyboard
·
Connectors
and cables.
The
structure of a CPU:
|
CPU |
Registers |
Computer
|
Input/ Output |
|
Arithmetic and Login unit |
System Bus |
||
|
Internal CPU Interconnection |
CPU |
||
|
Control Unit |
Memory |
Main Components in a CPU:
·
Control
Unit: controls the operations of the CPU and the computer
·
Arithmetic
and Logic Unit (ALU): performs
the computer’s data processing functions.
·
Registers:
provide storage internal to CPU
·
CPU
interconnection: Mechanism that provides for communication among the control unit, ALU, and registers.
Schematic diagram of a Mainboard:
What is a Microprocessor?
A microprocessor is a digital machine that can execute many
different software commands and control many types of electronic devices.
A sensible structured device that can be used as a
processing unit or a computer unit:
Contains an integrated chip.
Includes such a processor with memory and related circuits.
Microprocessor results:
The advent of the microprocessor has had a profound effect
on almost every aspect of our lives.
Today, even the most common activities are performed under
its direction and therefore, our lives are surrounded and dependent on
microprocessors.
CPU vs. Microprocessor:
Most CPUs in modern
IT are multicore processors, meaning integrated circuits have two or more
processors attached to help improve performance.
Microprocessor single
use CPU.
CPUs tend to perform basic tasks, the most powerful of which
is the way we are presented (usually the machine code), most likely using
complex calculations (such as a floating-point), and capable of combining
dynamic objects. The whole system is set up as such CPU systems to perform
large, unobtrusive tasks.
· Most CPUs are microprocessors but not every microprocessor is a CPU.
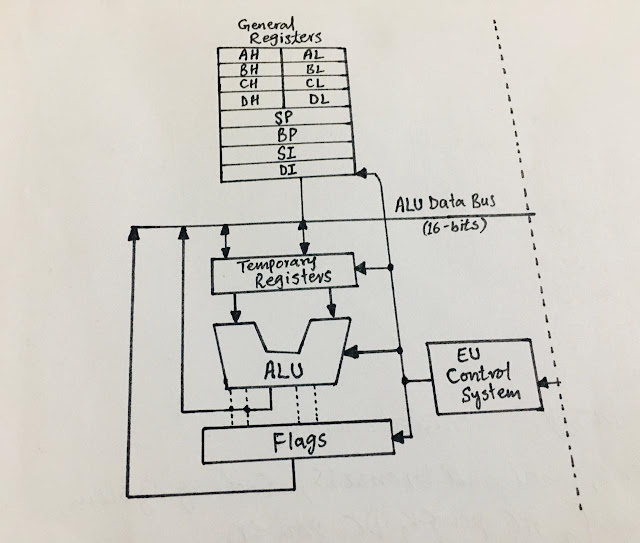
Schematic diagram of a Microprocessor:
Applications of Microprocessor:
Many devices show how dependent on the
micro-processing we have become nowadays;
·
Pocket calculators
·
Digital watches (some with calculators built-in,
GPS)
·
Cell phones (iPhone)
·
CD and MP3 players (iTunes)
·
Home security and control devices (Intercom)
·
VCRs and DVD players
·
Personal computers (Laptop, iPad)
·
Digital cameras.
Main memory;
PC/ server use “DRAM” (Dynamic RAM)
·
SDRAM
·
DDR SDRAM
·
RDRAM (RAMBUS DRAM).
Main memory;
·
Embedded computers use DRAM or SRAM (or both)
depending on applications.
Storage;
·
Secondary storage
·
Non-volatile
·
Stores programs, a magnetic disk (hard-disk) is
usually used
·
In embedded computers, “flash” memory or “ROM”
is usually employed.
Hardware and Software:
·
What is
Hardware?
The physical components of the
microprocessor-based systems are called hardware.
·
What is
Software?
Software is something that we
install onto our computer that has its own code, like a specific program. It’s
the programs and applications that we run on a physical device.
·
Both of
they have decision making capability by executing a program or completing a
task.
What are the
differences between hardware and software?
Hardware vs. software
|
Basis |
Hardware |
Software |
|
Definition |
Hardware is a physical device that is capable of operating tasks and
executions based on the software |
Software is a set of instructions that are given to the computer to
perform operations |
|
Types |
Output, input, storage, processing, and control devices |
Programming software, system software, and Application software |
|
Examples |
CD-ROM, monitor, printer, video card, scanners, and label makers |
Apple maps, Adobe Acrobat, QuickBooks, Google Chrome, Microsoft Word,
Microsoft Excel, |
|
Development |
Hardware is made up of electronic components |
Software is developed by writing instructions in a programming
language. |
|
Replacement |
If Hardware is damaged, it can be replaced with a new one |
If Software is damaged, it can be replaced with its backup copy. |
|
Durability |
Hardware wears out over time |
The software does not wear out over time. However, bugs can affect it. |
|
Nature |
Hardware is physical in nature |
Software is logical in nature. |







Comments
Post a Comment
if you have any doubt, please let me know.