8086-Microprocessor ppt, It's features and architecture.
8086-Microprocessor Architecture, Features and Architecture:
Objective:
After reading this and our upcoming content you will learn:
· The Architecture of 8086 CPU (the operation of the
execution unit and the bus interface unit).
·
8086 CPU Registers (the internal registers
array).
·
Features of 8086 Microprocessor.
Introduction:
The 8086 microprocessor is a 16-bit machine with a 16-bit
data bus and 20-bit address bus. This allows for 220, or 1MB of addressing
space. The 8086 processor has the capability of operating in minimum mode or
maximum mode. Both modes have different ways of dealing with external
buses.
8086 microprocessor family has a typical basic structure,
8086 processor’s arrival on the computer scene has quickly taken the lead in
the personal computer market.
8086 processor is used everywhere, from a dedicated control
systems to fast network file servers.
The Pentium offers compatibility with all previous 8086
machines, with many new architectural improvements.
Intel 8086 microprocessor, developed by Intel Corporation,
has three versions:
1.
Intel 8086: 5 MHZ
2.
Intel 8086-2:
8 MHZ
3.
Intel 8086-4:
4 MHZ.
8086 microprocessor have different memory organization, to
master how to access memory and I/O.
The execution unit (EU) and the bus interface unit (BIU)
allow the 8086 to execute software more efficiently than earlier 8-bit
microprocessors.
Whenever the 8086 is reset, the processor fetches its first
instruction from address FFFF0H and sets the interrupts disabled. On the
PC, this address points to boot instructions in the motherboard’s system ROM, which
begins the process of booting DOS.
Features of 8086 Microprocessor:
A 16-bit 8086 has a 20-bit address bus can access up to 2020
memory locations (1 MB). (Address ranges from 00000h to FFFFFH).
Support up to 64K I/O ports.
Provides 14, 16-bit registers. (Word size is 16 bits and double
word size is 4 bytes).
Has multiplexed address and data bus.
8086 is designed to operate in two modes:
·
Minimum
·
Maximum
It can pre-fetches up to 6 instructions bytes from memory
and queues them in order to speed up instruction execution.
It requires a +5V power supply.
An operating prototype circuit on a solderless bread-board incorporating
four DIP ICs, a DIP LED bar graph display (upper left), and DIP 7_segment
display (lower left) is shown in the picture below:
A 40 pin dual-in-line package.
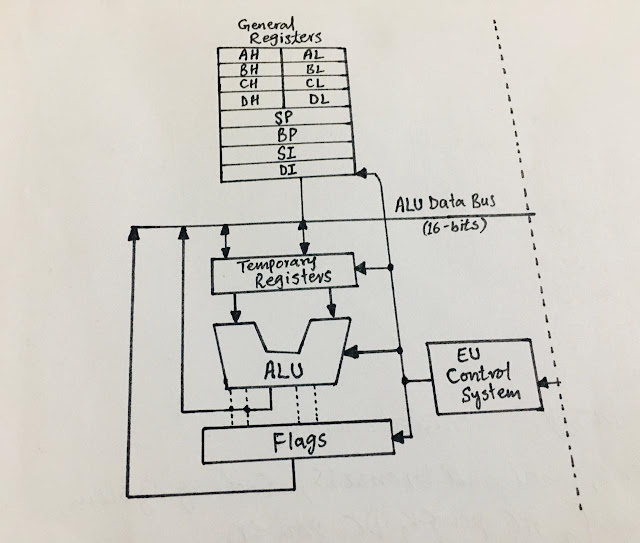
The Architecture of 8086 includes:
·
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU).
·
Flags
·
General registers
·
Pointer and index registers
·
Flag registers
·
Segment registers
·
Instruction byte queue.
The internal architecture employs parallel processing that
is, implemented with several simultaneously operating processing units.
It can directly access 1MB of memory.
The memory used by the 8086 microprocessor is 1 MB and each byte
can be addressed uniquely with 20-bit addresses.



Comments
Post a Comment
if you have any doubt, please let me know.